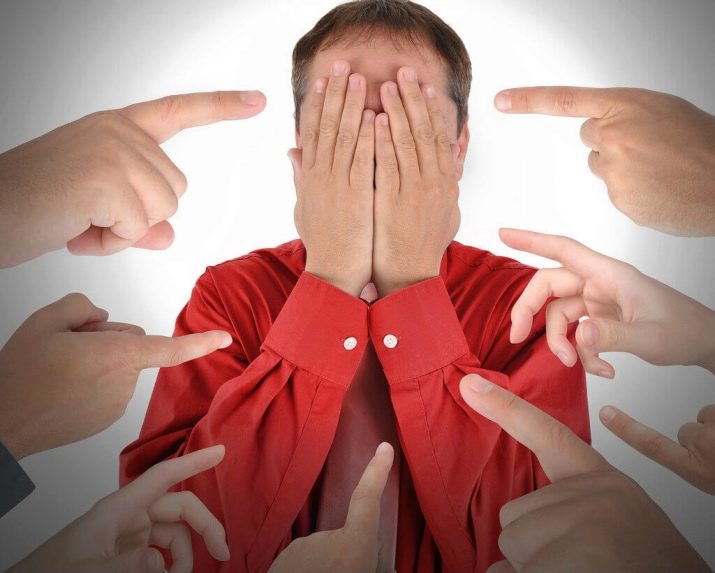
Anthropophobia is one of the worst fears in fear of people. The one who is afraid of insects, can not go to the dense forests, and the one who is afraid of air travel can use trains and buses. However, living in complete isolation from people will not work.
What it is?
Anthropophobia can occur in different ways: from mild discomfort among people to tangible physical symptoms, including nausea or dizziness. Fear of people can spread to all members of humanity, but more often the patient with anthropophobia is afraid of specific social groups or of all strangers.
Fear of narrow categories of people is called in its own way, depending on the specific profession, gender, age. Anthropofobs usually combine fear to at least several social groups.
Fear is treated by psychologists quite successfully, but the duration of treatment will depend on the degree of development of the phobia and on its causes.
The causes of anthropophobia, unlike many other phobias, are very variable. Often this is a consequence of injury.
The concepts of anthropophobia and social phobia are often confused, although they are quite close and sometimes complement each other. However, these concepts should be distinguished, since it is a bit easier for a social phobia to exist in our world than to a real anthropofoba.
The fear of a society of people (this is how the concept of social phobia stands for) consists experiencing intense fear, panic, and obsessive anxiety while in a particular group or large group. However, anthropophobic issues are more complicated: for such a patient, even one person’s company may be uncomfortable.
If a social phobia is disturbed by various social situations and crowds of people in one place, anthropofobs are afraid not only to interact with another person, but simply to be near. Fears are associated with difficulties in understanding the intentions of another person: it seems to the patient that all people represent a danger to him.
Often a phobia occurs in people with a low level of empathy, who cannot understand the emotions of others, and may be accompanied by paranoia.
Sometimes a phobia of people occurs in insecure individuals who are afraid of being misunderstood, ridiculed or humiliated. In this case, they also avoid contact with people, but even just a passing person can be a potential threat. Usually, it is ineffective to treat specifically anthropophobia - professionals understand its deepest causes and find out which personality traits prevent a person from feeling comfortable in human society.
Causes
Most often, anthropophobia begins in adolescence. Since during this period, the psyche is most vulnerable and a person gets a lot of new experience and new information, at the age of 12-17 years many start to frighten both the society in general and people in particular. In equal measure, both young people and girls can become ill with anthropophobia. Sometimes a phobia disappears by itself as it gets older, but often it remains for the rest of its life in one way or another, until a person turns to a psychologist.
There are also cases where adults acquire anthropophobia after experiencing negative events.
Experts call, first of all, to look for the causes of anthropophobia that appeared at any age in childhood. Unfavorable and difficult conditions of growing up, an unfriendly conflict situation for a child in a family - many factors can become the ground for the formation of neuroses. Very often the cause becomes experienced physical abuse, other psychological trauma, severe stress associated with people in one way or another: all this can be a serious impetus for the development of such a phobic disorder.
Having survived an unfavorable situation or being in a hostile environment, which can be a family or school, over time the child comes to the conclusion that being alone with him is safer, more comfortable, calmer than with anyone else. Nothing is a threat, no need to expect a dirty trick, you can relax, be yourself and not try to adapt to the imposed norms of behavior.
This eventually leads to complete social isolation if the problem is not solved.
The further the phobia develops, the more difficult it is for a small person to get rid of distrust of peace and wariness. Over time, all curiosity about human society disappears. Moreover, in loneliness, a person can easily neglect social norms: if such behavior was established in childhood, in an adult state, even after successful treatment of a phobia, the restoration of communication and social skills also takes a lot of time and effort.
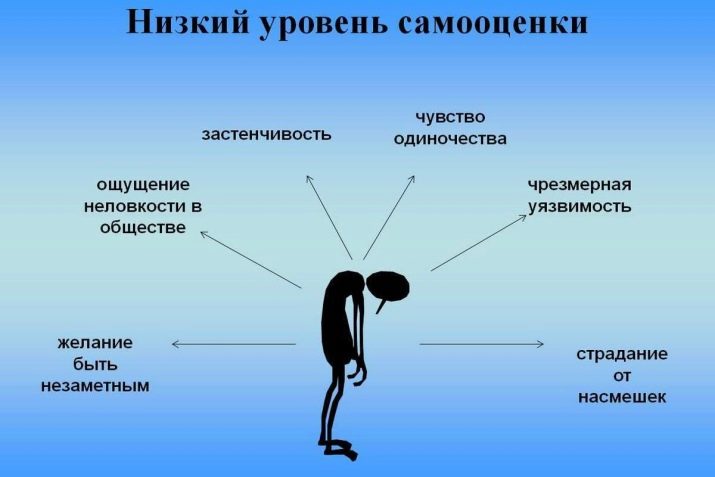
Some psychologists believe that it is mainly this disorder that occurs in people whose self-esteem has been greatly underestimated.
Frequent aggressive criticism and complete rejection by respected or close people provokes a negative feeling of strong self-doubt. As a result, being close to people, the patient constantly expects some kind of trick, aggression, negative. It seems to a person that the rest condemn him, from which he behaves defiantly and strangely for society, and people really begin to condemn him.
The patient is confirmed by his thoughts and the phobia is only getting worse. Breaking the vicious circle independently without the help of psychologists in neglected cases is almost impossible, however, In addition to the work of a specialist, support and understanding from relatives are a very important factor.
Anthropophobia can sometimes develop against a background of coptophobia - it is an obsessive fear of getting into an uncomfortable position, suffering shame, being ridiculed,
In extreme cases, this phobia is accompanied by a phobia at all to somehow stand out from the majority; a person tries to be inconspicuous and completely loses his individuality. Those suffering from such a phobia often perceive the features of their appearance or behavior negatively, they are afraid to become an object of ridicule. It is the fear of not being accepted that often underlies anthropophobia.
It is worth noting that severe childhood experiences do not always lead to the development of strong neuroses - Sometimes a person copes with them himself in the early stages and preserves mental health. And sometimes phobias develop in those in whose fate they had no preconditions: even if the child grew up in a good family, he did not face moral and physical violence.
In this case, it is the personal qualities that come to the fore - those features that make a person predisposed to fear of people, such as shyness or suspicion. In such situations, a slight shock may be sufficient for the development of a phobia.
Symptoms
Psychologists have the answer to the question of what anthropophobia itself is and what its distinctive features may be. Symptoms of anthropophobia can vary only in combination with other mental disorders (for example, schizophrenia and other psychoses, autism, bipolar disorder or dementia).
In such cases, psychologists individually work with each patient, considering the problem as a whole.
In most cases, all people have a phobia about the same and goes along with the following obsessive fears.
- Fear of all people at all. This kind of panic or discomfort can even make a patient see a stranger approaching on the street, and communication with people or physical interaction is perceived even more acutely.
- Fear of strangers, strangers. A person suffering from a disorder of such a plan may find it difficult to build new social connections for himself. Any contact with new people is accompanied by obsessive anxiety, and sometimes trembling, dizziness, nausea.
- Fear of touching others often also accompanies anthropophobia. Often this fear is the result of injury. It is very difficult for such people to be in a crowd where strangers accidentally touch them: in severe cases, a phobia can be accompanied by physical pain.
- Fear of people with certain external features - for example, with curly hair, snub-nosed or chubby. Such external features for each person with a phobia will be very individual.
- Fear of people of a certain gender, age, nationality. It is also a disorder that is often associated with injuries in childhood or adulthood. For example, women who survived violence are often afraid of men afterwards.
Anthropofobs very often fear to look into the eyes of other people, they are also worried about the possibility that others will closely look at him or look into his eyes.
This happens primarily because anthropophobia is the fear of being condemned or ridiculed by others, acquaintances or strangers.
Only a professional psychologist or psychotherapist can establish an accurate diagnosis of anthropophobia. This disorder is very easily confused with others, so the experience of a specialist matters. It is extremely important to consider all possible criteria for this disease, since in advanced cases it is often mistaken for autism.
It is also important to remember that not always the unwillingness to communicate with anyone indicates a serious pathology. It is very dependent on the nature and temperament: for example, introversion is not considered a pathology. Only obsessive fear can be attributed to a phobia, which seriously prevents a person from living and socializing.
In certain periods of their lives, even healthy, completely socially successful and socially active individuals become victims of depression, are in a bad mood, which is why they temporarily avoid social ties. These conditions can not be attributed to pathologies.
To accurately diagnose anthropophobia, it is sometimes not enough to know the symptoms. It is also important to collect anamnesis, communicate not only with the patient, but also with his relatives, loved ones, close friends or colleagues. The living conditions of a person and his profession can also tell a lot to an experienced specialist.
Among other things, psychologists use the following diagnostic methods to determine anthropophobia.
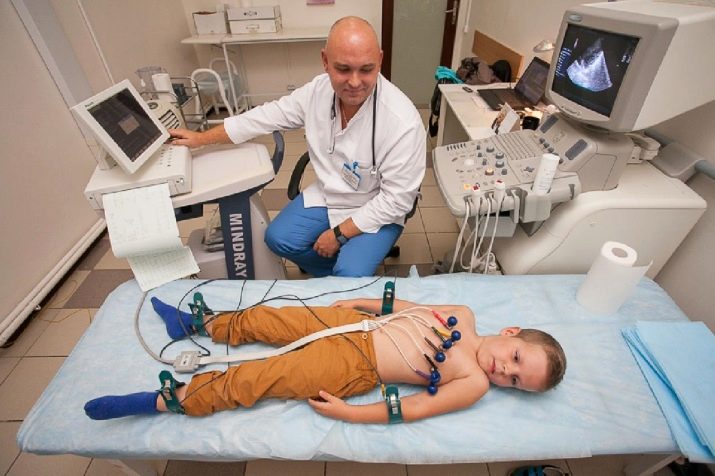
- ECG diagnostics, viewing computed tomography or MRI. Such measures can rather accurately assess the degree of stress or panic in an uncomfortable social situation for the patient. Data is collected on the condition of the cerebral vessels and on the impulses that occur in certain zones in the brain.
- The empirical method is simpler and often used. It is relevant in the presence of other disorders with similar symptoms.
- Patient questioning or testing - This is the main diagnostic method, which is the most affordable and versatile. However, the correct interpretation of the answers and tests is very important, and only a good specialist can competently produce it.
Forms of phobias
The forms of anthropophobia can vary depending on a person’s specific fears. For example, very often the following categories cause panic.
- Unknown strangers often become the subject of fear of anthropofoba. This is very uncomfortable, because we inevitably encounter strangers on a daily basis as soon as we leave the house. A separate problem is in the formation of new acquaintances - the patient will in every possible way avoid contact with new people and would prefer old friends.
- A crowd of people, too, often causes fear. This is due to the fact that anthropophobic opposes itself to others: a large crowd of people in this case leads to great anxiety. Over time, the anthropophobic will prefer not to appear in crowded places at all and will avoid them in every possible way.
- The fear of communication is also often part of anthropophobia. This is not about introverts who just need less social interaction than extroverts. The anthropophobic fear of communication will be pronounced, and the desire to reduce social contacts will be obvious, even to complete solitude.
- Fear of certain categories of people is also very common. This may be the fear of drunks, children, women, surgeons - anyone. Such fear is not always a form of anthropophobia, but in some cases, experts refer it to the fear of people. When diagnosing it is important to understand the causes. Very often, anthropophobic fear begins with one category of people, and then develops and spreads to others.
Obsessive fear of people is a phobia that can quickly or slowly develop and have several stages. The usual course of the disease begins with a mild stage, when the anthropophobe experiences a certain feeling of anxiety during a shopping trip, a trip in public transport or before going to a party where there will be many strangers.
This anxiety may arise even when communication is with one person, important and authoritative or, on the contrary, unpleasant for the patient.
Usually, many cope with a phobia at this stage on their own: the strength of a person’s will, his ability to self-analyze, and the support of his relatives are crucial here.
At the progressive stage of anthropophobia, it becomes much more difficult for a patient to control his actions and emotions in the presence of other people. If such a person has unexpected contact with new people, in this situation there is a high probability of an attack of aggression or, on the contrary, panic and anxiety. Sometimes in some patients with anthropophobia at this stage, undesired meetings lead to tearfulness, sweating, and palpable shivering.
To cope with a phobia at this stage is more difficult, since it is already beginning to manifest itself on the physical level.
Only professionals can help with the running stage.. Anthropophobia is extremely characterized by a significant change in a person’s lifestyle. A person with anthropophobia lives extremely isolated, prefers loneliness, rarely comes into contact even with those whom he knows all his life, including relatives, close friends or lovers.
If it is relatively easy to solve the problem in the early stages, in this case only compulsory treatment will be effective. Close ones should insist on a visit to a psychologist, since the patient himself no longer wants to change anything.
Treatment
To overcome the disease in the early stages, a person can himself with the support of loved ones. In neglected cases, consultation with a psychologist or even a psychiatrist is necessary to get rid of anthropophobia.
Sometimes medication may be required, but usually anthropophobia can be overcome with more simple means.
The following measures are recommended by experts to overcome the fear of people.
- Emotional relief will help in the early stages. A person must learn to control himself and think that others do not pose any real threat to him, as often as possible. It is important to consider obsessive fear from a rational point of view.It is good when there are close people who will support the anthropophobe and help him. Positive emotional reinforcement is very important - for example, vivid impressions and pleasant activities, one way or another connected with people.
- Breathing exercises can help with anxiety and panic attacks.. The exhalation should be twice as long as the inhalation, when the anthropofob feels the approach of intense anxiety. A close person who is nearby, at this time can duplicate the same breath, so that the patient is easier. This is an effective method for those cases where the phobia begins to manifest itself at the physical level.
- Physiotherapy can also help. At a minimum, psychologists advise to regularly take a contrast shower, do a massage. During anxiety, this will help to quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Well, if after a stressful situation, you can take a warm bath, and immediately at the moment of panic, a loved one will massage your back.
- Distraction methods can also work. Try to escape from the phobia: count the cars passing by, passers-by or objects to the room. You can pinch or stroke yourself to escape from panic.
- Phytotherapeutic effects - This is another auxiliary method, which is often practiced by psychologists with various kinds of phobic disorders. To reduce the fear of people, take valerian drops or herbal teas. These are safe tools to help relieve anxiety. According to the prescription of the attending physician, you can try more serious sedatives if other means do not help. In advanced cases, the doctor may recommend various tranquilizers, nootropics and antidepressants as a complex therapy.
For faster recovery, it is recommended to switch to proper nutrition, drink less alcohol, fried, spicy and sweet. Also very useful is yoga and breathing exercises.
In severe cases of anthropophobia, it is better to regularly talk with a psychotherapist, so that treatment is always under control.
It is most effective to overcome anthropophobia forever in the early stages of its manifestation. A very important step is the very awareness of the phobia and the need to interact with people. It is difficult at first, therefore the patient will need willpower, support of relatives and specialists. In order to prevent the appearance of a phobia, it is recommended to lead a healthy social life and avoid stress, and bring up the child in a friendly atmosphere.
On what is anthropophobia, see below.