Perhaps, there is no person in the world who is completely indifferent to the injections that he has to do. Light agitation, waiting for pain for at least a few seconds is a normal reaction to an effect that cannot be considered painless. But there are people (and there are a lot of them) who have the prospect of an injection, even if life depends on it, causing panic and uncontrollable horror.. This phenomenon is called trypanophobia.
Description
Trypanophobia is a mental disorder that is considered one of the most common in the world. This is a pathological fear of pricks, needles, syringes and injections.. According to medical statistics, about 15% of the world's inhabitants suffer from this fear. It is noteworthy that in countries where disposable syringes with thin needles that do not cause intense pain when pricking appeared earlier, the number of people suffering from this disorder is lower, for example, in the USA trypanophobia is diagnosed in 10% of residents.
In Russia and in the post-Soviet space, where for a long time thick metal needles of reusable syringes were used, the fear of injections is higher — up to 20% of our country's people suffer from trypanophobia. This suggests that This phobia is closely related to the quality of medical care. But this is not the only prerequisite for the development of disorder.
Usually trypanophobia develops in childhood, for this it is often called the fear of childhood. Trypanophobia should not be confused with iatrophobia - fear of doctors, fear of going to hospitals, examinations, testing, treatment.
Often, these two phobias go side by side, many jatrophobes fear not only people in white coats, but also injections. But many trypanophobes are not afraid of doctors and nurses, they can safely go to the clinic, go to the therapist if they are sick, take tests if they are not associated with punctures and injections.
But the purpose of injections can plunge a person into a state of acute anxiety, and attempts to drag him into the treatment room can result in a panic attack.
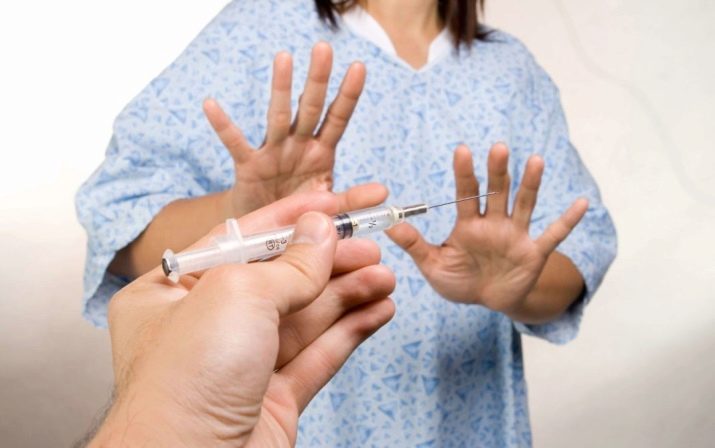
Trypanophob itself usually honestly admits that it is afraid of injections. Many of the people with this disorder do not see anything unusual in this; in their understanding, any person should be afraid of injections. But in a dangerous situation, people with trypanophobia lose the ability to control their behavior - they may faint at the sight of a syringe, start to break out and run away, some are hampered by such fear that they cannot cross the threshold of the treatment room. In any situation where the injections can be replaced with pills or anything else, trypanophobes will definitely take advantage of this.
Whether this phobia is dangerous is hard to say. As long as a person is healthy and there is no need for injections, his life is no different from the life of everyone else. This fear does not bother him in any way. But it is necessary to get sick, there is an urgent need for an injection, and the person falls into an anxious state.
Waiting for the injection is more painful for him than the injection itself. Some febs refuse injections in principle, despite the arguments and persuasion of doctors. And it is this refusal that can cause serious health problems and a threat to life.
There are drugs that can be taken only by injection or drip. There are situations in which delay can cost a patient life, and then an injection is the best way to quickly deliver the right drug to the patient’s body.
Signs of
It’s not so hard to recognize true trypanophobe.Many people say they are afraid to give injections, but these are just words. A real person suffering from trypanophobia does not like to talk about this topic, because even the thought of such a procedure as an injection, be it intravenous or intramuscular, causes him suffering. There are patients who are afraid of injections into the vein in panic, there are those who are afraid of piercing the buttocks, many successfully combine the fear of all types of injections, including blood sampling from a finger for a general analysis of scarifier.
People with this disorder try to plan their lives in such a way that they can avoid injections. If there is an opportunity not to go for vaccination, they will not go. If there is even the slightest chance to avoid undergoing medical examination, where they take blood for analysis, they will definitely take advantage of this.
The doctor who prescribes the treatment will try to try to see if it is necessary to make injections, if there is a chance to replace them with pills or medicine, if not, then he will recheck information from other doctors and on the Internet several times. Anxiety will increase, and eventually trypanophobe will certainly try to find an excuse and not go for injections. If this is not possible or the need for an injection has arisen suddenly, he cannot hide his horror.
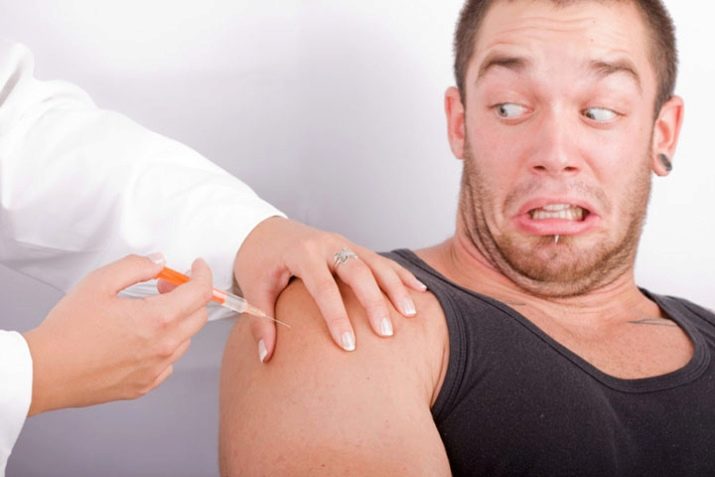
The lion’s dose of adrenaline is instantly released into the blood. Under his action quickly pupils dilate, hands begin to shake, lower lip. The skin becomes pale due to the outflow of blood (the body, with a danger signal, does everything to provide more blood to the muscles, because it is possible that it will be necessary to run or fight).
The heart begins to beat often, breathing becomes shallow, intermittent and shallow. The body temperature is slightly reduced, and the patient becomes covered with sticky cold sweat. Vomiting may begin, clouding and unconsciousness may occur, a promise of escaping and escaping may occur - the symptomatic picture is largely individual and depends not only on the severity of the phobia, but also on the character and personality of the person.
After a panic attack, patients with trypanophobia feel emotionally exhausted, tired, they are ashamed. They are critical of themselves, they are well aware of the absurdity of the situation, but they can do nothing so that the panic attack does not happen again. The brain itself starts these processes, they are mostly beyond the control of man.
What is so afraid of trypanophobe really? Not everyone is afraid of precisely the moment of puncture with a sharp needle of the skin. Some people feel a chilling horror at the thought that they are injected with a medicine through a needle, they literally feel how it spreads under the skin, over the muscles. They painfully perceive the injection procedure itself. Some fear that after the injection there will be bleeding, hematomas, bumps, prolonged pain.
Many people are afraid of infection with dangerous infections and small air bubbles that can get into the needle while taking a medicine. Sometimes it scares not only the whole process with all its stages, but also the very appearance of needles and syringes, even if they are not intended directly for a given patient - in the cinema, in pictures and photos.
Phobia is equally characteristic of both men and women. No significant gender difference observed. But in men, trypanophobes have one unpleasant feature - they are more prone to manifestations of panic attacks than women.
The fair sex behave, despite the horror, much more decent.
Causes
Fear of injections is formed in childhood, and the behavior of parents, temperament and character of the child contribute a lot to it. All babies make injections, for example, vaccinations. But some people endure it, cry, stink and soon forget about the injection, while others have a strong fear of repeating the situation. Children with increased excitability of the nervous system, a weak pain threshold, impressionable babies with a rich imagination and increased anxiety are more prone to developing phobias.
Such children can cause fear not only their own feelings from injections, but also stories, films, read books, photos. The terrible story of the "black hand", which was creeping into children's rooms and pricking children with a needle with poison, can cause intense experiences. The story will eventually be forgotten - the memory is arranged so that it erases unnecessary information that a person does not use. But at the subconscious level, there will remain a clear connection between needles, syringes and something terrible, deadly, with threat.
The behavior of the parents may be adequate (it is necessary to give an injection - we will do it), or it may be restless and experiential. Mom, who, before inoculation of a child, is more nervous than him, increases the level of anxiety in the child as well.
There are parents who tell the children that if they don’t eat or stop walking through the puddles, they will get sick and then they will have to go to the hospital to give injections. About injections in such cases, note that adults always say. If the child is suspicious and susceptible, such statements alone are enough for the rest of his life to remain panicked with the fear of manipulating syringes.
The reasons may lie in a negative personal experience - an unsuccessful injection, complications, the rudeness of the medical staff, and thick needles. In this case, the image of the syringe is directly related to pain. There is no other association. And to be afraid of pain is by and large a normal defense mechanism. Only in trypanophobes does it acquire abnormal, hypertrophied scales.
It should be noted that parents with such a problem most often raise children who have trypanophobia. It is not a matter of genetics, not of heredity, but of an illustrative example - the child accepts the model of the world and interactions with it offered by parents for good coin. Mom or father’s fear of simple medical manipulation can simply be taken on faith, then a persistent deep phobia is also formed.
In the future, the prospect of getting a shot in the buttock or vein will be perceived by the child as a very dangerous situation.
Methods of struggle
Calls to fight the fear of injections, pull themselves together by an effort of will and defeat the phobia, which the Internet is full of, in practice can do little to help true trypanophobes. The thing is that at the moment of danger they cannot control the manifestations of fear, therefore there can be no talk of any effort of will. Mental breakdown needs rendering qualified psychiatric and psychotherapeutic assistance.
The most effective method is considered cognitive behavioral psychotherapy. This technique helps to identify the true causes of fear. An experienced doctor will not call for overcoming horror, he will simply try to change the patient's key beliefs that cause a chain reaction of a panic attack. Occupations can be individual and group, in addition can be applied suggestion, hypnosis, NLP, patient training in autotraining, methods of deep muscle relaxation.
As soon as the first stage is left behind, the patient will gradually begin to be immersed in situations in which he will be surrounded by images and objects that had previously frightened. And well, if at first a person can talk about injections without excitement, then he can pick up a syringe, and then allow himself to be given an injection of vitamins intramuscularly.
In addition to psychotherapy can be applied drug treatment - antidepressants are prescribed to relieve anxiety and depression symptoms. If you have noticed signs of fear of injections in a child, you should not ignore them and wait until the child “outgrows fears”. Seek help from a psychologist. The “younger” the phobia, the easier it is to get rid of it.
Effective techniques of art therapy and fairy tale therapy, as well as play therapy, for example, playing a doctor, help children.