Dogs are known to be excellent hunters. And perfectly oriented in space. Their senses help them in this. The dogs' eyes are not of paramount need for analyzers, but his abilities are rather high, although they are inferior to human ones.
Eye structure
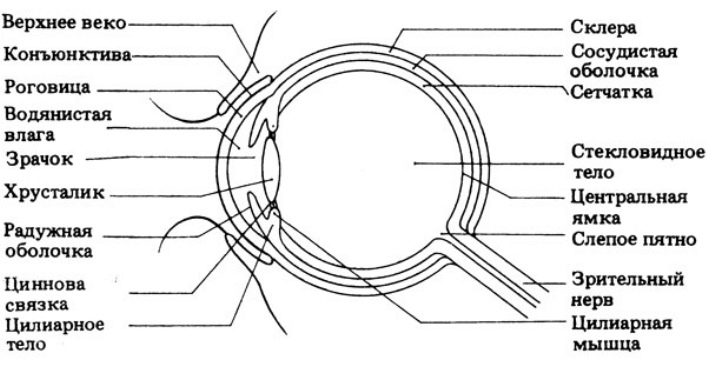
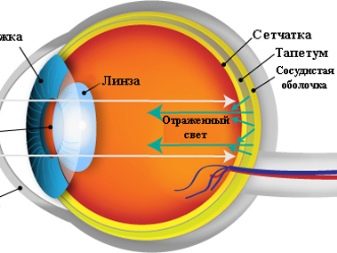
Anatomically, the dog's visual analyzer is very similar to that of a human. The cornea is located in front of the eyeball - this is its outer shell. Normally, it is clean, transparent and shiny. Its purpose is to protect the eyeball from damage. Also, the outer shell is involved in the refraction of light.
Under the cornea is the middle layer of the eye - the iris. In its center is the pupil, and behind it - the lens. In addition, the iris forms a network of blood vessels that feed the eye.
Muscle fibers are attached to the lens. Shrinking and relaxing, they change its curvature, providing a vision of objects at different distances.
The pupil and lens are directly involved in the visual perception of the surrounding reality. The luminous flux, passing and refracted through them, falls on the retina, where it is converted into the corresponding signals.
The retina is the third layer of the eyeball. Its complex design allows you to modify the visual impulses and transmit them to the brain. Here is formed the final picture of the world.
In addition to the above-mentioned eye elements, bringing the eyes of the animal and man together, there are other strictly specific to dogs.
So, the eye of a quadruped has an additional outer shell called the third eyelid.. It is a thin film that envelops the eye. It protects it from dust and dust. And constantly moisturizes, thanks to the lacrimal gland.
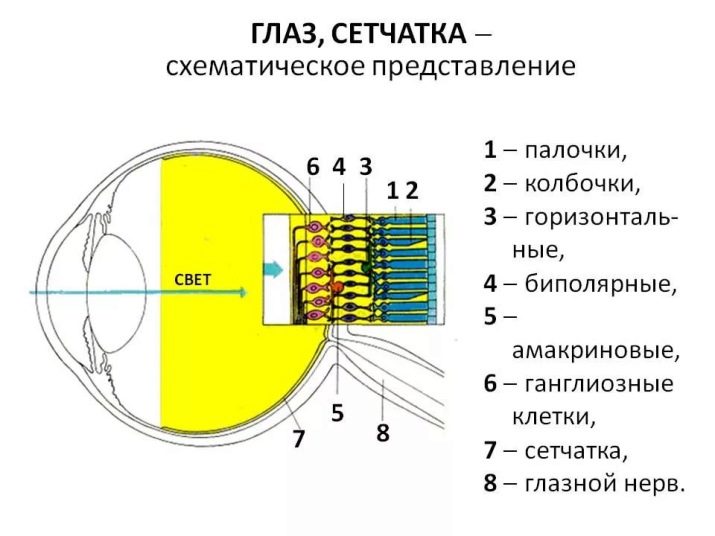
The retina deserves special attention. Its features provide a specific vision of the world around dogs.
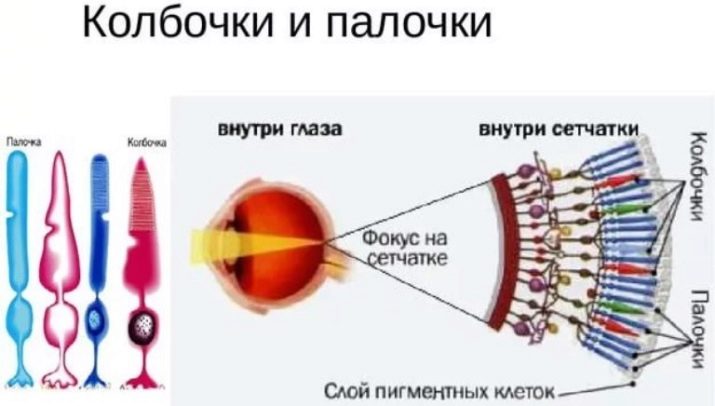
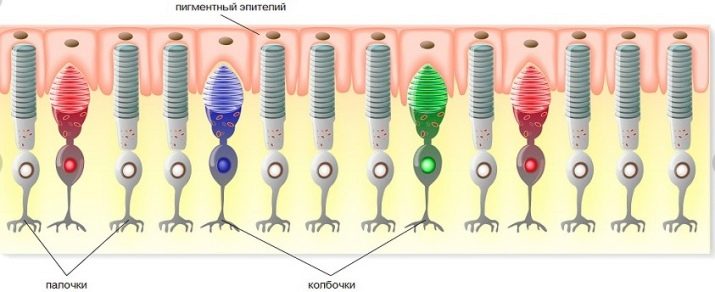
As it is known, certain cells in the structure of the retina, called rods and cones, are responsible for the color perception and orientation in the twilight.
Cones are responsible for the color perception of objects during the day, and the sticks are responsible for visual orientation at night. In quadrupeds, rods predominate in the net structure. There are several times more of them here than in humans. As for the cones, their number is much less.
Also, the caudate have no yellow spot, which in humans is located in the center of the retina and is an accumulation of cones. But there is an additional crystalline layer called tapetum. It performs a special role in the visual adaptation of the animal.
Conventionally, the retina is divided into 2 parts:
- top - provides the dog with a visual orientation in the dark, responsible for visual acuity;
- lower - is responsible for day vision.
The eyes of our beloved pets are arranged in such a way as to help them quickly navigate in space and not to miss the prey. It is laid by their original nature of a wild predator and a clever hunter.
Do colors distinguish?
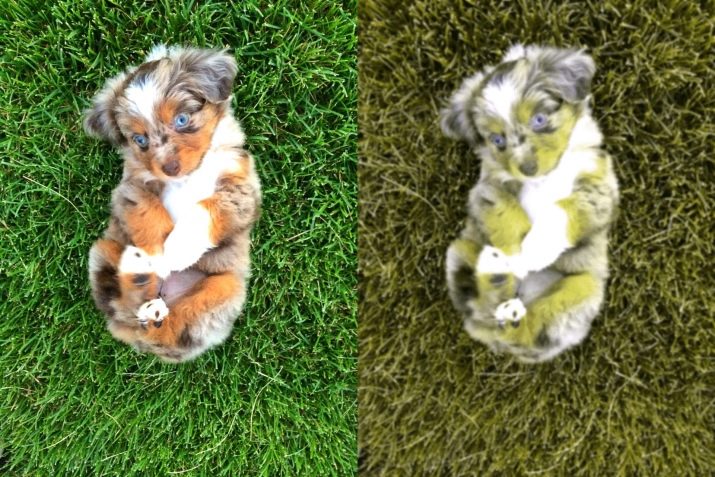
The statement that the vision of our beloved pets is black and white is erroneous. Dogs see and analyze the world in different colors, even though their palette, compared to a person, is rather scarce.
To begin with, retinal cones provide color vision for dogs. But their number is negligible.
In humans, these cells have 3 types:
- picks up the long waves of the color spectrum and determines the red, orange tones;
- reacts to medium waves of yellow, green colors;
- sensitive to short, blue-violet waves.
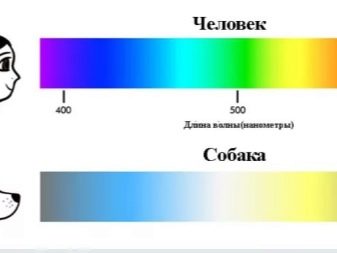
In dogs, there are only 2 types of cones.
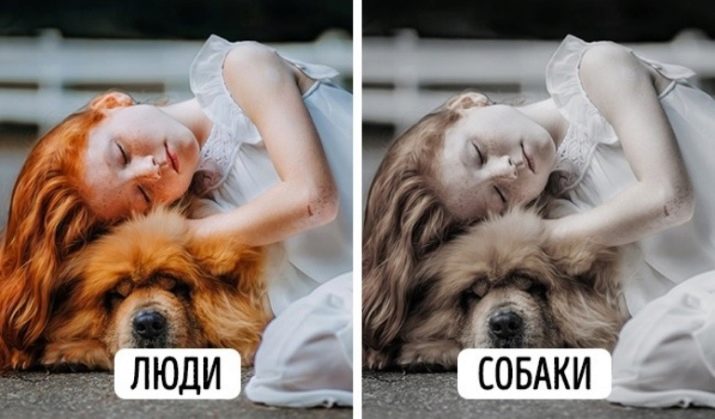
Green and red shades are not subject to perception of a dog. He perceives them in white or gray. But the blue, purple and yellow colors of the dog are perfectly distinguished. Thus, they manifest selective color blindness, and their vision can be compared to that of people with color blindness.
How in this case to explain the fact that the dogs are oriented in the traffic light signals? There are even special breeds - guides accompanying people with poor eyesight. The fact is that in this case the dog-guide does not react to a change of color, but to a change in the brightness of the signal. And it helps them competently assess the situation.
Dog owners more than once noted a change in the behavior of four-legged pets at the sight of a certain color. For example, the dog reacted sharply to people in yellow clothes. This also confirms their color vision.
Such a dog's "preference" in colors with the use of trainers used in their work. Using in the process of practicing toys and attributes of colors to which their wards are sensitive, they manage to achieve positive results much faster.
How does the lighting?
The dog’s vision is universal, as this animal is satisfactorily oriented both day and night.
Orientation in the dark
Night vision is well developed in dogs. This is achieved with rods, present in the structure of the retina in large quantities. It is so large that dogs see at night and distinguish objects four times better than people.
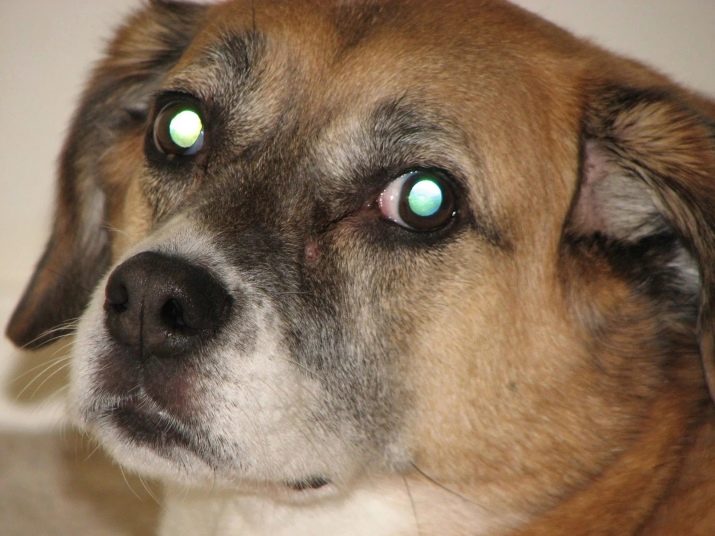
It is wonderful to see the tapetum already mentioned in the complete darkness of the dogs. This is a reflective membrane, which is compared with the glow of headlights or specular coating. It is located in the upper part of the retina, responsible for night vision.
Light, passing through the retina, is reflected on it through the membrane again. Thus, the image is clearer and more contrast.
Animals see objects at night in gray. And they demarcate, almost without exception, all of its 50 shades.
Daylight
In the afternoon, the four-legged ones are also well oriented. And I must say that it is easier for them than for people. The human eye is sensitive to too bright light. It is hard for us to look at the sun with wide eyes, we have to squint.
In dogs, the lower part of the retina contains dark pigment, which allows to neutralize the excessive flow of bright light. Therefore, they are much less susceptible to harsh light.
Another feature of the animal's eyes is the glow when the light beam hits them. You may have noticed that at certain times your pet's eyes begin to glow yellow or another color. At the same time, they turn into monochromatic circles, in which even the pupil is not visible.
The reason for this is, again, a reflective membrane, thanks to which dogs are so well oriented in the dark. The color of the glow can be yellowish, as well as with green and brown-brown shades. Or combine several colors at once: at the top yellow or green, at the bottom - green-blue. This is due to the color of the membrane. In dark-eyed animals it is darker than in breeds with a light iris.
Range and width of sight
In addition to the fact that dogs do not perceive a decent range of colors and are well oriented in the dark, their vision has other features. This time they are associated with clarity and breadth of perception.
Dog can not boast of visual acuity. The reason for this is the absence of a yellow spot on its retina, characteristic of the human eye. It is here that a large number of cones are concentrated. Thanks to the yellow spot, we have the opportunity to see objects both near and far (if we are talking about a healthy person).
The retina of dogs lacks a yellow spot, and therefore their visual acuity is useless.
In order for a dog to clearly see any object, it must be at least 30 cm away from it. From which it was concluded that visibility in these animals is akin to people with a slight degree of farsightedness. However, despite the difficulty of focusing on nearby objects, dogs cleverly estimate the distance to the target.
Another property of a dog's eye is the perception of a moving object. His dog identifies and at a distance of 900 m. Excellent property for hunting breeds. But if the same target is immobilized, then the caudate can see it no further than 600 meters. The visibility of objects in dynamics is provided by a large number of sticks in a dog's retina.
They also determine the panoramic vision of the four-legged. That is, they perceive the image of the entire retina due to the absence of a yellow spot.
As for the latitude or field of view, in dogs it averages 250 °. This is significantly more than in humans. And depends on the location of the visual axis of both eyes. In animals, they diverge at an angle of 20 °, while in humans they are parallel. A large degree affects the shape of the visual field. It is not round, like a human, but has oval outlines, which becomes a significant advantage during the hunt - it allows you to view more space.
But the field of view is not the same for all breeds. This figure varies based on the structure of the dog's skull. The narrower the muzzle and the longer the nose, the higher the degree of visual latitude.
How do dogs see people and the world around them?
If for a person the eyes are 90% of the information, then for the four-fingered eyesight is not at all in the first place. Much more important for them hearing and scent.
However Dogs visually adapt well in space. They distinguish individual colors, perceive distant static objects. However, their vision provides certain goals. Its main task is fixation on dynamic objects, that is, moving in space.
By the way, it's not for nothing that they say that when an angry, grinning dog rushes at you, first of all, stop. This way you will be less attractive to her.
Dogs living in the wild and domesticated individuals perceive the world around them in the same way. And even their favorite pet owners close up are perceived by them as a blurred outline. A devotee dog recognizes his master from a thousand not by his facial features, eye color, or nose shape, but by completely different criteria.
It is interesting that in 1 second the dog's eye perceives 80 frames. Compared to human, this is 56 frames more. Therefore, four-legged friends are completely uninteresting TV, because the frame rate in it is 60 Hz. The picture on the screen of fluffs is obtained as a blur.
Although some modern TVs have a frequency of 100 Hz and are available for watching doggies. Currently being developed to create a "dog" programs. They will help pass the leisure four-legged, when their masters are busy.
The main differences from human vision
The structure of the organ of vision of humans and dogs are very similar. And coincide in all major indicators. But small differences make the dog and human vision of the world around us fundamentally different.
- Their main difference is the difference in the color spectrum. In humans, it is much larger, due to a large variety of cones.
- The predominance of the chopsticks of the furry helps them to orient themselves several times in the darkness of the night than to the person, while distinguishing objects in fairly clear outlines.
- Visual acuity of shaggy is significantly lower than in humans.
- But dogs can boast a breadth of the field of view, 70 ° higher than the human figure.
- Human vision is perfect. It allows you to see far and near, to share a sea of colors and shades, to perceive objects of any size and configuration. The dog's eye does not see well near. And instantly perceives moving objects.
These are the main criteria that distinguish our vision from the dog. Such differences are caused primarily by the purpose of the organ of vision, which for us and for them has different meanings.
How to check eyesight
The eyes of the caudate, as well as in humans, undergo changes that can cause destructive processes and reduced vision. There are several reasons for this: age, injuries, certain diseases, including infections.
Recognize the visual problem with a pet you can even at home. Understanding that your dog's eyes are out of order will help, above all, the appearance of visible changes in the organ itself. These may include heavy discharge from the eyes, tearing, suspension of the upper eyelid, redness or blurred eyes. Such phenomena almost always affect the ability of visual perception.
Understand that the animal has become bad to see, and its behavior. Elementary, watch how the dog moves. In case of problems with vision, her movements will become timid and insecure. Pet will begin to stumble on the corners, it will be difficult for him to fit into the doorway.
To dispel all doubts about the ability of the dog to adequate vision, there are special tests.
The easiest way is to move your hand in front of a dog muzzle. If there is no response from the animal, and there will be no reaction of the pupil to the change in the intensity of light from the held hand, you should consider.
Another test involves creating an obstacle course of individual objects. One person releases the animal at the beginning of the distance, and the other, at the end of the strip, calls out to him. How accurately, bypassing all obstacles, the pet will pass this distance, will speak about the presence or absence of eye changes.
It is worth noting that home experiments will only allow you to suspect your dog’s vision problems. After that, you should seek help from a specialist. Using special equipment, he will determine the nature of the violation, establish a possible cause and suggest ways to solve the problem.
It is probably wrong to say that dogs see the world around them better or better than we are. Their vision is radically different from ours. But nevertheless, it gives them the opportunity to perfectly adapt and exist in the outside world, to be on guard of order and to master some “professions”.
Interesting facts about dogs' vision are waiting for you in the video below.